For those who take a fish oil supplement everyday or eat a decent amount of fresh fish, it can be assumed that it is all created equal.
Unfortunately – this is just not the case.A lot of people consider all fish oil supplements the same. The only difference is the cost. So why spend more on a ‘quality’ fish oil, rather than just picking up a value pack from the chemist?
FISH SOURCES
A major difference between inferior fish oils and superior fish oils is the source. The fact is, all fish oils can actually be separated into several different types, or grades, dependent on the source of the oil. These grades vary dramatically in quality, consistency, safety and effectiveness.
Whilst increasing fish consumption can offer health benefits, there are concerns associated with fish and shellfish consumption due to contaminants such as methyl mercury, dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) – all pollutants from industrial processes. Those fish that sit higher in the food chain are likely to contain higher levels of contaminants and some larger fish such as shark, marlin, swordfish and tuna are becoming increasingly unsafe to eat. High toxin levels in larger, longer living fish therefore means that we are restricted as to how much we can eat and how often.
Fish also contains vitamin A, which is a fat-soluble vitamin and is stored in the body. High levels of vitamin A are toxic and have been associated with liver damage. In purified oils, vitamin A is removed, enabling high quantities of omega-3 to be consumed without risking vitamin A toxicity. This is particularly important for pregnant women, as excess intake of vitamin A during pregnancy can cause birth defects.
When considering a fish oil supplement, it is important to note that some contain higher levels of contaminants than others. Only truly pure oils will be contamination-free. Oils sourced from larger longer living fish such as salmon will generally contain the highest level of contaminants. Oils should ideally be sourced from fish lowest in the food chain such as anchovies. Small, short-lived fish also tend to be more sustainable.

Generally, the cheap kinds of fish oils are sourced from sharks, cod, tuna, salmon and other ‘waste’ fish sources – all of which are known to contain high levels of mercury and other contaminates. These fish are all quite large in size, and therefore will accumulate more toxins through what they eat than the smaller fish mentioned above will.
PURIFICATION
In order for a fish oil to be virtually free from contaminates, it must undergo an extensive (and often expensive) filtration and distillation process during manufacture.
Levels of contamination is a concern we see expressed time and time again, and for good reason. The best fish oils undergo a lengthy molecular distillation process that separates dangerous mercury and lead from the oil, while concentrating it for higher omega-3 levels, so you know that you are only swallowing fish oil, and nothing else.
Molecular distillation is an expensive process, which is why many cheaper brands do not undertake it. Without proper distillation, the fish oils can contain high levels of dangerous contaminates.
Unfortunately, there is very little that can be done to stop this evasion from happening, and these cheap fish oils continue to be rolled out.
Only after this precise molecular distillation process has been undertaken, and when the fish oil is regularly tested and passed to have low levels of contamination can they be referred to as ‘Pharmaceutical Grade Fish Oil’.
Because of the process, you can be sure that even the smallest particles of contamination are removed, resulting in a fish oil that is approximately 1000 times more pure than any chemist grade fish oil.
TOXICITY
Heavy metals like mercury, lead, arsenic and pesticides are considered oxidants. They are detrimental to your health, attacking healthy cells and causing illness and disease. Recent attention on antioxidants and ‘free radical damage’ has highlighted the importance of reducing oxidants in the body.
Unfortunately, for those who are taking an antioxidant supplement, a cheap fish oil may be erasing all your hard work.
On the other hand, a top, pharmaceutical-grade fish-oil derived omega-3 supplement is actually one of nature’s best antioxidants. It has the ability to cross the blood brain barrier, helping to prevent the incidence of strokes, heart attacks and inflammatory conditions.
Another possible source of oxidants in cheap fish oils are are rancid fats. The types of fats (polyunsaturated) in fish oil are very susceptible to oxygen, heat and light, therefore high-grade fish oil manufacturers use specific manufacturing practices such as nitrogen flushing to ensure fish oils are protected from oxidation throughout the entire production and transport process.
In the production of low grade fish oil, these measures may not be taken, leaving you with harmful oxidised (rancid) fats. A fishy smell to your fish oil capsules or liquid indicates the product may be rancid.
CONCENTRATION & RATIO
An obvious difference between a good fish oil and a ‘great’ fish oil is the strength. Don’t be fooled by the ‘each capsule contains 1 gram of fish oil!’ claims. If each tablet weighs 1 gram, then of course it contains 1 gram of fish oil. The difference is in the concentration of omega-3’s in that capsule.
The top pharmaceutical-grade fish oils contains high ratios of omega-3 fatty acids in the form of EPA (eicosapentanoic acid) and/or DHA (docosahexanoic acid). For example two capsules of Pharmepa RESTORE contains 1000mg of EPA and 1 capsule of Pure Essentials Omega 3 contains 410mg of EPA and 250mg of DHA
In comparison, a cheaper brands contain ratios like or less than 180mg of EPA and 120mg of DHA. Though it may seem cheaper, you’ll need to take 2 - 10 the same amount of capsules, along with the fact they most likely have not undergone mollecular distillation. And you think you’re saving yourself money...
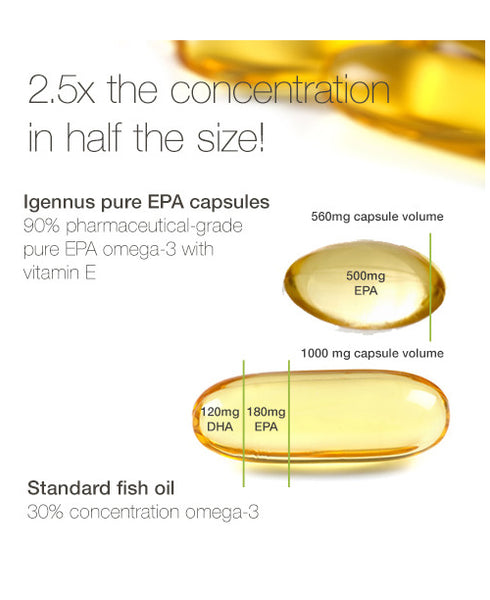
For specific health concerns, athletes or maintenance of general health, fish oil needs to contain appropriate ratios of EPA or DHA for the purpose. It is known that EPA is important for the treatment and reduction of inflammation, reduction of strokes and heart attack prevention. DHA is important for foetus development, cognition and brain development. Many cheaper brands simply ‘throw in’ what they can get.
EPA & DHA DURING LIFE STAGES... WHAT TO TAKE AND WHEN.
Our requirements for EPA and DHA change throughout life and so does the optimal amount of each fatty acid in our diet.
Children require DHA for growth and development, and the brain, CNS and retina rely heavily on the adequate supply of DHA during growth in the womb. Thus women should emphasise DHA in their diets when they become pregnant and continue to take this until they cease breastfeeding. Children continue to need DHA up until the age they start school, so if children under the age of five are taking an omega-3 supplement, it should contain DHA. The exception is for children with developmental problems – where pure EPA or high EPA omega-3 has been shown to be most effective for supporting cognitive function. We would still recommend, where possible, naturally derived sources of omega-3 such as oily fish to support a balanced EPA and DHA intake.
“EPA levels are under constant demand and low EPA levels in adolescents and adults correlates strongly with development of mental health issues, including depression, dyslexia and dyspraxia, heart problems, joint and bone conditions, as well as neurodegenerative diseases such as MS and Parkinson’s.”
After the age of five, the development of the brain and CNS starts to reduce and the body’s need for DHA reduces. This is a good time to increase EPA in the diet, as studies show that EPA can help with childhood behaviour and academic performance, as well as focus, attention and reducing aggression. Dry skin conditions, asthma and allergies are also common in children and good levels of EPA at this time can help reduce the inflammation associated with these issues.
Between the ages of five and 65, the majority of the body’s needs can be met by using EPA-rich oils and eating fish, marine products, organic greens and pastured animal products. EPA levels are under constant demand and low EPA levels in adolescents and adults correlates strongly with development of mental health issues, including depression, dyslexia and dyspraxia, heart problems, joint and bone conditions, as well as neurodegenerative diseases such as MS and Parkinson’s. EPA also protects our genes and cell cycle, as well as helping to keep our stress response regulated, so an adequate supply of EPA throughout adult life can help prevent a range of chronic illness.
In later life, cognitive function and brain deterioration may become a concern. Once again, maintaining high levels of EPA has been shown to lower the risk of developing and worsening cognitive decline and dementia. If, however, you know someone who already has a diagnosis of dementia or Alzheimer’s, their brain has already been damaged and needs structural support. At this point, DHA becomes important again and taking a high-EPA product that contains 250mg of DHA also is important to prevent further loss of brain tissue.
KNOW YOUR OMEGA 3 FORMS: TG, PL, EE vs rTG
There are three main forms of omega-3 fat found in supplements, including triglycerides (TG, the natural form of fish oil), ethyl-esters (EE, the concentrated form of fish oil) and phospholipids (PL, derived from krill oil). The more recently developed re-esterified triglyceride (rTG) takes the EE form of omega-3 and reconverts it back to its natural TG form. This not only allows the delivery of concentrated omega-3, but ensures that absorption is optimised.
There are numerous studies comparing the absorption of these different forms, measured by their ability to raise the omega-3 index (the % of EPA and DHA in our red blood cell membranes) based on a standard manufacturer-recommended dose. rTG has proven to be the most effective, followed by EE, then TG and finally PL from krill oil.
Using a triglyceride fish oil is adequate for anyone looking for general wellbeing support, but since the concentrations of EPA and DHA are not high, standard fish oil does not raise the omega-3 index sufficiently to offer significant health benefits. For more intensive support, an ethyl-ester form of omega-3 will allow very high doses of EPA and DHA to be achieved as concentration can be as high as 90% (compared to 18% in a standard triglyceride fish oil). High concentration is important because this influences absorption and increases the omega-3 index (% of EPA + DHA in red blood cells) and the targeting of benefits specific to a certain active (for example EPA). Purification and esterification also reduce to a minimum the volume of unnecessary fatty acids, waste products and impurities within the oil. Re-esterified triglyceride omega-3 concentrates the oil to a very pure form, like ethyl-ester, but minics the natural triglyceride form to offer both high concentration and superior bioavailability.
Unlike lower concentration standard fish oil supplements, Igennus 70-90% EE and rTG supplements enable therapeutic blood plasma levels of omega-3 to be achieved. When taking EE omega-3, absorption can be enhanced by taking capsules with foods containing fat. For therapeutic use in specific health conditions, rTG is the gold standard – thus, it is also more expensive but has been proven to raise the omega-3 index to a greater extent and more rapidly than any other form of omega-3 – as with Pharmepa RESTORE
WHAT'S THE REAL COST?
If you are going to take a fish oil supplement (or any supplement), you should get the best quality available. As you would have read, buying fish oil is not as simple as just grabbing the cheapest off the shelf.
Omega-3 fatty acids are extremely beneficial to your health, but if you purchase a low-grade product that contain many contaminants or rancid fats, you could just end up doing yourself more harm than good.
By investing in a premium fish oil, you can be sure that it is one of the best on the market.
In this economic-focused climate, it can be tempting to just grab the cheap, bulk pack from the chemist, but we hope that this article stands to show the disadvantages and dangers of doing just that.
On the subject of expense, you need to devote some brain power to what you are really getting out of each capsule. Don’t just look at the big picture – it all comes down to actual concentrations. Some of the fish oils we offer are up to 10 times as strong as cheap brands.
The bottom line? Educate yourself. Stop wasting your money on cheap, nasty fish oils and invest in the BEST fish oil you can buy.


